Vacuum blood collection is a vacuum negative pressure blood collection, the use of a large number of automatic instruments and blood preservation put forward higher requirements on the stability of original blood samples, so that the vacuum blood collection technology has broken through the requirements of safety only. The accuracy, original character of specimen, maintenance time, fit of tube machine and test tube strength can be used to evaluate the quality of vacuum collection.
The classification of vacuum blood collection
1. Common serum tube with red cap and collection vessel without additives is used for routine serum biochemical, blood bank and serological tests.
2. The rapid serum tube with orange cap has coagulant in the blood collection tube to accelerate the coagulation process. The rapid serum tube can coagulate the collected blood within 5 minutes, and is suitable for serological serialization test in emergency.
3. Inert separation glue and coagulant booster are added in the blood collection tube with golden cap. After the specimen is centrifuged, the inert separator gel can completely separate the liquid components (serum or plasma) and solid components (red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, fibrin, etc.) in the blood and completely accumulate in the center of the test tube to form a barrier, and the specimen remains stable within 48 hours. Coagulant can quickly activate coagulation mechanism, accelerate coagulation process, suitable for emergency serum biochemical test.
4. The heparin anticoagulant tube has a green cap and heparin is added to the blood collection tube. Heparin directly has the effect of antithrombin and can prolong the clotting time of specimens. Suitable for erythrocyte brittleness test, blood gas analysis, hematocrit test, erythrocyte sedimentation and general biochemical determination, not suitable for blood coagulation test. Excessive amounts of heparin can cause an accumulation of white blood cells and cannot be used for white blood cell counts. It is also not suitable for leukocyte classification because it can make the background of blood plate stain light blue.
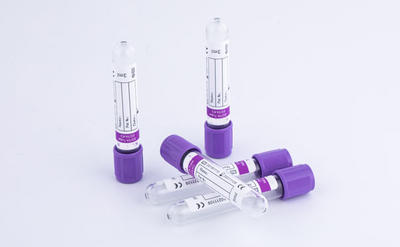
5. Plasma separation tube with light green cap, adding heparin lithium anticoagulant into the inert separation hose can achieve the purpose of rapid plasma separation, which is the best choice for electrolyte detection, and can also be used for routine plasma biochemical determination and emergency plasma biochemical detection in ICU. Plasma samples can be loaded directly into the machine and remain stable in cold storage for 48 hours.
6. EDTA anticoagulation tube purple cap, EDTA (EDTA, molecular weight 292) and its salt is a kind of amino polycarboxylic acid, which can effectively chelate calcium ions in blood samples. Chelating calcium or removing the calcium reaction site will block and stop the endogenous or exogenous coagulation process, so as to prevent the coagulation of blood samples. Suitable for general hematology test, not suitable for coagulation test and platelet function test, also not suitable for calcium ion, potassium ion, sodium ion, iron ion, alkaline phosphatase, creatine kinase and leucine aminopeptase determination, suitable for PCR test.
7. Sodium citrate coagulation test tube light blue cap, sodium citrate mainly through chelating with calcium ions in blood samples to play an anticoagulant effect. Applicable to coagulation tests, national Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, NCCLS) recommended anticoagulant concentrations of 3.2% or 3.8% (equivalent to 0.109mol/L or 0.129mol/L) and a 1:9 anticoagulant to blood ratio.
8. Sodium citrate esR tube black cap, esR test requirements of sodium citrate concentration is 3.2%(equivalent to 0.109mol/L) anticoagulant to blood ratio of 1:4.
Potassium oxalate/sodium fluoride gray cap, sodium fluoride is a weak anticoagulant, usually with potassium oxalate or sodium iodate combined use, the ratio of sodium fluoride 1, potassium oxalate 3. This mixture of 4mg prevents 1ml blood from clotting and inhibits glycolysis for 23 days. It is a good preservative for blood glucose measurement and should not be used for urease determination of urea, nor for alkaline phosphatase and amylase determination. It is recommended for blood glucose testing.
Post time: Nov-10-2021