Abstract: Objective To study the feasibility and safety of using absorbable hemostatic clip in laparoscopic cholecystectomy, and to provide data support for its clinical promotion. Methods a total of 97 patients who underwent elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy from December 2013 to December 2014 were selected as the study subjects, and they were divided into two groups according to their medical treatment numbers,49 patients with odd medical treatment numbers were selected as the observation group. Forty-eight patients with an even number were included in the control group. According to the groups, absorbable hemostatic clip and titanium clip were used for hemostasis during operation respectively, and the hemostatic effect and safety data were compared and analyzed after operation. Results The bleeding rates of the two groups were 18.4% and 16.7%, respectively. The observation group was slightly better than the control group, but there was no significant difference (P>0.05), that is, the hemostatic effect was significantly different. The incidence of complications in the two groups was 12.2% and 29.2%, respectively. Compared between groups, the observation group was significantly lower than the control group (P<0.05), that is, the safety of the observation group was significantly better than the control group. Conclusion The domestic absorbable hemostatic clip has advantages of good hemostatic effect and high safety in laparoscopic cholecystectomy, and it is safe and feasible for clinical use.
Intraoperative hemostasis is an important part of laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which not only directly affects the success of the operation, but also may endanger the patient's life. Although the traditional titanium clip hemostasis has a good hemostasis effect, it remains in the body for a long time, resulting in a high incidence of complications, so it needs to be further improved. The invention and application of absorbable hemostatic clip can fundamentally reduce the complications caused by hemostatic operation. Although its value has been confirmed by clinical and relevant studies, it lacks necessary data support for clinical promotion [1]. This study aims to confirm the value of domestic absorbable hemostatic clip in laparoscopic cholecystectomy and provide data support for its promotion. The contents and conclusions of the study are briefly described as follows.
1. Data and methods
1.1 General Data a total of 97 patients with elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy from December 2013 to December 2014 were selected as the study subjects, including 52 males and 45 females. The age range was 43-68 years, with an average of (52.6±10.3) years. The course of disease ranged from 12 to 49 months, with an average of (26.5±8.4) months. There were 48 cases of gallstone and 49 cases of gallbladder polyp. 38 patients had a history of epigastric surgery. All subjects were diagnosed and treated with laparoscopic elective surgery, and all of them met the relevant requirements of informed consent and medical ethics [2]. The subjects were randomly divided into two groups, and there was no significant difference in the basic clinical data between the two groups (P>0.05), indicating comparability.
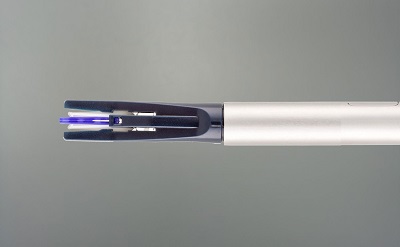
1.2 Methods All subjects underwent conventional laparoscopic cholecystectomy and perioperative nursing. Subjects in the observation group were treated with hemostatic clamps (SmAIL absorbable hemostatic ligation clamps made in China), and 1-3 hemostatic clamps were given according to patients' conditions. Subjects in the control group were treated with 1-2 titanium clips for hemostasis. The specific hemostatic operation was performed in accordance with the clinical routine operation.
1.3 Data Processing Methods SPSS18.2 statistical software was used to analyze the research data. The measurement data were expressed as' X ± S 'and t test was used. The counting data were expressed as X(%) and X2 test was used. When P<0.05, the difference was significant.
Results 2.
2.1 Hemostatic effect The bleeding rate of patients during surgery was taken as the evaluation content of hemostatic effect, and the bleeding rate was inversely proportional to the hemostatic effect. The bleeding rate of subjects in the two groups were 18.4% and 16.7% respectively. Although the observation group was slightly better than the control group, there was no significant difference (X2 =0.049,P=0.186>0.05), that is, the hemostatic effect was significantly different.
2.2 Safety 15d after surgery, the site of hemostatic clamp was observed by b-ultrasound, CT and other imaging methods. The incidence of tissue liquefaction, calcification and pain in this site were used as the safety evaluation content, and the incidence was 12.2% and 29.2% respectively. The observation group was significantly lower than that of the control group (P<0.05), that is, the safety of the observation group was significantly better than that of the control group. See the next article for specific data.
Post time: Dec-27-2021