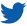
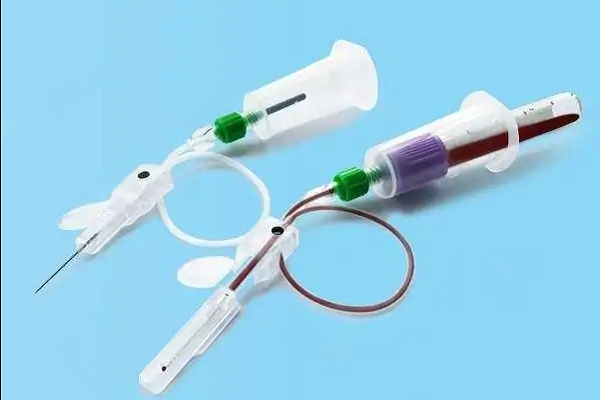
Vacuum blood collection vessel is a disposable negative pressure vacuum glass tube that can realize quantitative blood collection. It needs to be used together with venous blood collection needle.
Principle of vacuum blood collection
The principle of vacuum blood collection is to draw the blood collection tube with head cap into different vacuum degrees in advance, use its negative pressure to automatically and quantitatively collect venous blood samples, and insert one end of the blood collection needle into the human vein and the other end into the rubber plug of the vacuum blood collection tube. Human venous blood is in the vacuum blood collection vessel. Under the action of negative pressure, it is pumped into the blood sample container through the blood collection needle. Under one venipuncture, multi tube collection can be realized without leakage. The volume of the lumen connecting the blood collection needle is very small, so the impact on the blood collection volume can be ignored, but the probability of countercurrent is relatively small. For example, the volume of the lumen will consume part of the vacuum of the blood collection vessel, thus reducing the collection volume.
Classification of vacuum blood collection vessels
As shown in Figure 1, there are 9 types of vacuum blood collection vessels, which can be distinguished according to the color of the cover.
Figure 1 types of vacuum blood collection vessels
1. common serum tube red cap
The blood collection vessel contains no additives, no anticoagulant and procoagulant components, only vacuum. It is used for routine serum biochemistry, blood bank and serology related tests, various biochemical and immunological tests, such as syphilis, hepatitis B quantification, etc. it does not need to shake after blood drawing. The type of specimen preparation is serum. After blood drawing, it is put into 37 ℃ water bath for more than 30min, centrifuged, and the upper serum is used for standby.
2. orange cap of rapid serum tube
There are coagulants in the blood collection vessels to accelerate the coagulation process. The rapid serum tube can coagulate the collected blood within 5 minutes. It is suitable for a series of emergency serum tests. It is the most commonly used coagulation promoting test tube for daily biochemistry, immunity, serum, hormones, etc. after blood drawing, it can be reversed and mixed for 5-8 times. When the room temperature is low, it can be put into a 37 ℃ water bath for 10-20min, and the upper serum can be centrifuged for standby.
3. golden head cover of inert separating gel accelerating tube
Inert gel and coagulant were added to the blood collection vessel. The specimen remained stable within 48 hours after centrifugation. The coagulant can quickly activate the coagulation mechanism and accelerate the coagulation process. The sample type is serum, which is suitable for emergency serum biochemical and pharmacokinetic tests. After collection, mix it upside down for 5-8 times, stand upright for 20-30min, and centrifuge the supernatant for use.
4. black cap of sodium citrate ESR test tube
The required concentration of sodium citrate for ESR test is 3.2% (equivalent to 0.109mol/l), and the ratio of anticoagulant to blood is 1:4. It contains 0.4ml of 3.8% sodium citrate. Draw blood to 2.0ml. This is a special test tube for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. The sample type is plasma. It is suitable for erythrocyte sedimentation rate. After drawing blood, it is immediately reversed and mixed for 5-8 times. Shake well before use. The difference between it and the test tube for coagulation factor test is that the concentration of anticoagulant is different from the proportion of blood, which can not be confused.
5. sodium citrate coagulation test tube light blue cap
Sodium citrate plays an anticoagulant role mainly by chelating with calcium ions in blood samples. The concentration of anticoagulant recommended by the National Committee for clinical laboratory standardization is 3.2% or 3.8% (equivalent to 0.109mol/l or 0.129mol/l), and the ratio of anticoagulant to blood is 1:9. The vacuum blood collection vessel contains about 0.2ml of 3.2% sodium citrate anticoagulant. The blood is collected to 2.0ml. The sample preparation type is whole blood or plasma. After collection, it is immediately reversed and mixed for 5-8 times. After centrifugation, the upper plasma is taken for standby. It is suitable for coagulation test, Pt, APTT and coagulation factor test.
6. heparin anticoagulation tube green cap
Heparin was added to the blood collection vessel. Heparin has the effect of antithrombin directly, which can prolong the coagulation time of samples. It is used in emergency and most biochemical experiments, such as liver function, kidney function, blood lipid, blood glucose, etc. It is applicable to red blood cell fragility test, blood gas analysis, hematocrit test, ESR and general biochemical determination, not suitable for hemagglutination test. Excessive heparin can cause leukocyte aggregation and cannot be used for leukocyte counting. It is not suitable for leukocyte classification because it can make the background of blood slice dyed light blue. It can be used for hemorheology. The sample type is plasma. Immediately after blood collection, reverse and mix it for 5-8 times. Take the upper plasma for standby.
7. light green head cover of plasma separation tube
Adding heparin lithium anticoagulant into the inert separation hose can achieve the purpose of rapid plasma separation. It is the best choice for electrolyte detection. It can also be used for routine plasma biochemical detection and emergency plasma biochemical detection such as ICU. It is used in emergency and most biochemical experiments, such as liver function, kidney function, blood lipid, blood glucose, etc. Plasma samples can be directly put on the machine and kept stable for 48 hours under cold storage. It can be used for hemorheology. The sample type is plasma. Immediately after blood collection, reverse and mix it for 5-8 times. Take the upper plasma for standby.
8. potassium oxalate / sodium fluoride gray cap
Sodium fluoride is a weak anticoagulant. It is usually used in combination with potassium oxalate or sodium ethyliodate. The proportion is 1 part of sodium fluoride and 3 parts of potassium oxalate. 4mg of this mixture can prevent 1ml of blood from coagulation and inhibit sugar decomposition within 23 days. It can not be used for urea determination by Urease method, nor for alkaline phosphatase and amylase determination. It is recommended for blood glucose detection. It contains sodium fluoride, potassium oxalate or EDTA Na spray, which can inhibit the enolase activity in glucose metabolism. After blood drawing, it is reversed and mixed for 5-8 times. After centrifugation, the supernatant and plasma are taken for standby. It is a special tube for rapid determination of blood glucose.
9. EDTA anticoagulation pipe purple cap
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA, molecular weight 292) and its salt are a kind of amino polycarboxylic acid, which is suitable for general hematology tests. It is the preferred test tube for blood routine, glycosylated hemoglobin and blood group tests. It is not applicable to coagulation test and platelet function test, nor to the determination of calcium ion, potassium ion, sodium ion, iron ion, alkaline phosphatase, creatine kinase and leucine aminopeptidase. It is suitable for PCR test. Spray 100ml of 2.7%edta-k2 solution on the inner wall of the vacuum tube, blow dry at 45 ℃, take blood to 2mi, immediately reverse and mix it for 5-8 times after blood drawing, and then mix it for use. The sample type is whole blood, which needs to be mixed when used.
Post time: Jun-29-2022